- Product
Interactive boards. Fully customizable.
Capture, prioritize and follow up improvements.
Report and manage incidents. Visualize reports and statistics.
Operationalize your strategies and integrate your whole organization.
Access your tools in Microsoft Teams.
Customized templates. Problem solving, business development etc.
Manage project individually or in portfolios with visual and interactive tools.
Create and share best practices, one-point-lectures and standards.
Easy access to tasks, improvements and incidents.
Integrate DigiLEAN with your existing IT systems.
Meeting the demand of larger organizations.
High security level by default.
In less than 4 min
- Use Cases

Interactive tools for both shop floor and administration.
Visual project management.
Maintain standards. Manage incidents and discrepancies.
Manage tasks, integrate with problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Lean daily management tailored for healthcare.
Team task management, problem-solving and visualization.Case management, improvements, problem-solving, and strategy alignment.We have a LEAN solution for you too. Just ask!
We meet the demand of larger organizations.
- Pricing
- Shop Floor
- Product
Interactive boards. Fully customizable.
Capture, prioritize and follow up improvements.
Report and manage incidents. Visualize reports and statistics.
Operationalize your strategies and integrate your whole organization.
Access your tools in Microsoft Teams.
Customized templates. Problem solving, business development etc.
Manage project individually or in portfolios with visual and interactive tools.
Create and share best practices, one-point-lectures and standards.
Easy access to tasks, improvements and incidents.
Integrate DigiLEAN with your existing IT systems.
Meeting the demand of larger organizations.
High security level by default.
In less than 4 min
- Use Cases

Interactive tools for both shop floor and administration.
Visual project management.
Maintain standards. Manage incidents and discrepancies.
Manage tasks, integrate with problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Lean daily management tailored for healthcare.
Team task management, problem-solving and visualization.Case management, improvements, problem-solving, and strategy alignment.We have a LEAN solution for you too. Just ask!
We meet the demand of larger organizations.
- Pricing
- Shop Floor
Lean Thinking
Lean thinking is a phrase you meet many places. We will help you undestand what it’s about and put it into context of other familiar and relevant lean principles.
What is lean thinking
Lean thinking is basically the concept of lean where the mindset is focusing on the operations as a whole. Instead of optimizing departments, function areas or locations separately, the entire value chain is considered as a whole when designing the processes.
Customers and customer value is a core principle in lean and comes before product focus. The customer is therefore a vital part of the process and lean thinking.
Lean thinking is supported by the 5 principles of lean, and the people come first. The concept was extended from functional level to business level and five principles were defined:
- Define customer value
- Identify value streams
- Create flow
- Implement pull
- Continuously improve – aim for perfection
People value
A core value from lean is the people, the employees. Without people, you have no organization. Without an organization, you have no business.
Lean thinking emphasize on employees motivation and morale through “purpose”. Adding purpose to each individual will also fulfill people’s needs for self-actualization according to Maslow’s pyramid of needs, resulting in higher motivation.
Each employee must be given a clear vision of their purpose in the organization. A clear definition of their value and contribution in the common goal of providing customer value.
Another perspective here is to develop and utilize the people to the extent of their potential. This means that workers should be given the opportunity to grow, develop and move to new responsibilities
Customer value
“Customer” is the keyword here. What gives value in the eyes of the customer? If you can help a customer create value, it will create value for you. This is the basis for the first principle of lean thinking.
This idea is quite far from those who define value within their department. And it’s not uncommon.
If you don’t have a solid market dialogue already, you should engage your customers in your delivery or products. Your customers are the voice of the market. They are the decision makers and the force behind the pull principle. This is the only validation of how to meet the market, solve problems for-, and create value for the customers.
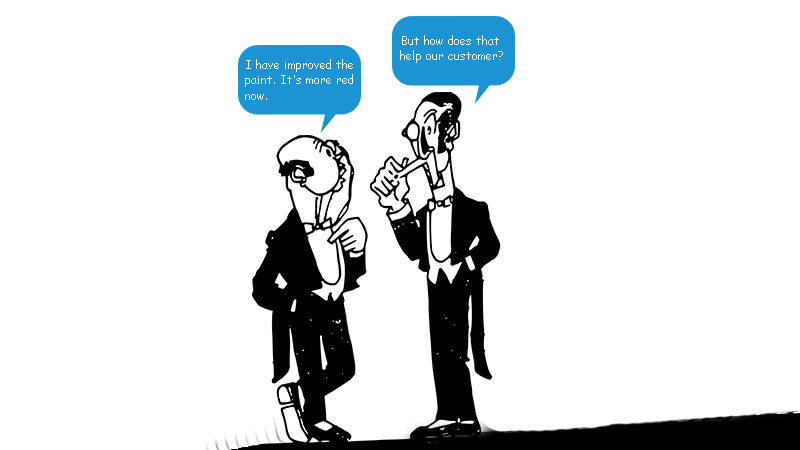

Change and adapt processes
In the process of implementing lean and build a lean thinking culture, things most likely have to change. With the customer value re-discovered, you must identify your current processes. This involves your whole value chain, vendors, contractors, supply chain, the lot. Get the full overview, and perform value stream mapping (VSM). A value stream map visualize all your processes, transactions, deliveries and activities from raw material to a commercial product or delivery.
According to the lean principles, this is where you identify the true value creating activities, and thus the waste.
Use the VSM to baseline and revise your process flow. This will be the recipe to achieving operational excellence, increased efficiency and results.
Implementation
It’s not that easy. Lean thinking and VSM doesn’t give a definitive answer. It’s a basis for decisions taking you to the point where theories are being tested.
It is important to embrace the lean thinking attitude at this stage. It implies a mindset that allows and plan for failure with the agility to adapt and change direction as required. In the process, it’s important to ask “why?” when the results are not as expected. Learning to understand the cause and effect is critical to be able to manage and navigate your business forward, and leading to success.
Another challenge in the implementation is managing the business and workforce in the process. First and foremost taking ownership and showing the commitment and belief in lean thinking is a critical success factor to get your employees onboard. Starting implementation in pilots or smaller, more controllable groups are typically more manageable than going all in from the beginning. This enables you to establish best practice, expose faults, issues and challenges in a scale where it is under control, and subsequently create a better experience for the whole workforce when rolling out changes full scale.
It works, what now?
Lean thinking isn’t just a lean project with a defined scope, objective, goals and a deadline. Implementation of lean, or any kind of improvement is a continuous process (Kaizen). And this is where the employee engagement really comes into play. By encouragement, autonomy and authority to contribute and affect the improvement work in your organization, more and better knowledge is put into the “suggestion box”. This adds a proportional opportunity for the company to increase the level of value creation in the continuous improvement work.
Implementing a new philosophy like lean thinking is also a continuous process by itself. It’s a company culture that must be build, and probably takes years. A culture is something that saturates the organization. It’s something that will automatically be induced to new employees through words, language and attitude of fellow employees. To achieve this, it requires relentless focus, continuous improvement, success and celebration.
So, it’s two-fold. Both the culture and value stream needs continuous improvement focus to stay competitive. For some organization it’s all about production, efficiency, quality, for some it may be creativity, innovation and new products. But common for all is they can all use lean thinking to increase performance.
© 2025 DigiLEAN AS
